
If you have installed Python 2.x, run python -m SimpleHTTPServer 8000.

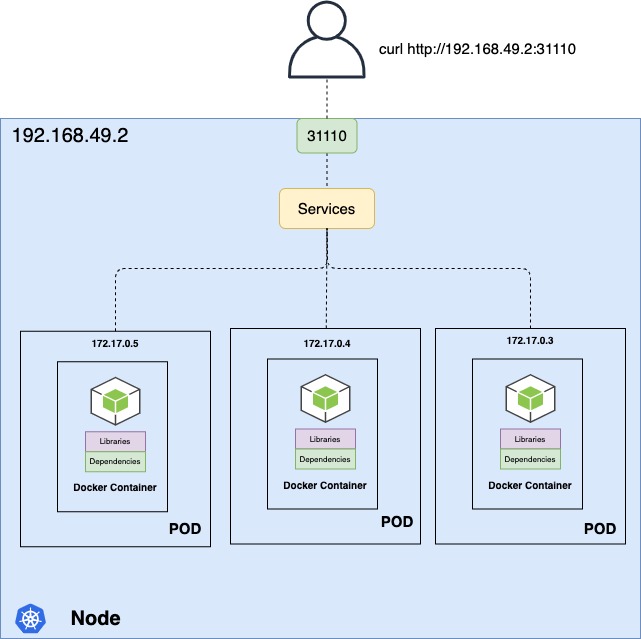
Run the following command to start a simple HTTP server on port 8000. If you have installed Python on your machine, use the following instructions as an example to connect from a container to a service on the host: This is for development purpose and will not work in a production environment outside of Docker Desktop for Mac. we need to expose port 80 using NodePort service like following.
#DOCKER FOR MAC NODEPORT WINDOWS#
You can find further instructions for Windows & macOS here. Enabled addons: dashboard, default-storageclass, storage-provisioner. which resolves to the internal IP address used by the Preparing Kubernetes v1.18.2 on Docker 19.03.8. Use Healthchecks, Secrets, ConfigMaps, placement strategies using Node/Pod affinity / anti-affinity.
Be able to run stateless and stateful applications on Kubernetes.
#DOCKER FOR MAC NODEPORT SOFTWARE LICENSE#
With the in-your-face popup to force upgrade Docker and the software license change, it was time to look elsewhere for local Kubernetes development needs. Install and configure Kubernetes (on your laptop/desktop or production grade cluster on AWS) Use Docker Client (with kubernetes), kubeadm, kops, or minikube to setup your cluster. Even though it eats CPU and memory like crazy and makes the fans go wild. We recommend that you connect to the special DNS name I have been using Docker Desktop to enable Docker and Kubernetes in Mac for quite some time now. The host has a changing IP address (or none if you have no network access). There are two scenarios that the above limitations affect: I want to connect from a container to a service on the host The docker (Linux) bridge network is not reachable from the macOS host. VirtualBox lets you run virtual machines on your Mac (like running Windows inside macOS, except for a Kubernetes cluster.) Skip to step three if everything has worked to this point. Run brew cask install virtualbox in your Terminal. Per-container IP addressing is not possible Install VirtualBox for Mac using Homebrew. This interface is actually within the virtualĭocker Desktop for Mac can’t route traffic to containers. If you are on a different platform like Linux, or using VirtualBox instead of Docker for Mac, the instructions to install Minikube may be slightly different. This tutorial also assumes you are using Docker for Mac on macOS. There is no docker0 bridge on macOSīecause of the way networking is implemented in Docker Desktop for Mac, you cannot see aĭocker0 interface on the host. This tutorial uses Minikube to create a local cluster. After changing IPs, it is necessary to reset the KubernetesĬluster and to leave any active Swarm.
The internal IP addresses used by Docker can be changed via the Settings (Windows) Networking stack, along with some ideas for workarounds. Access the KinD clusterīy default, the cluster access configuration is stored in $/.kube/config if $KUBECONFIG environment variable is not set.Services : web : image : nginx:alpine volumes : - type : bind source : /run/host-services/ssh-auth.sock target : /run/host-services/ssh-auth.sock environment : - SSH_AUTH_SOCK=/run/host-services/ssh-auth.sock Known limitations, use cases, and workaroundsįollowing is a summary of current limitations on the Docker Desktop for Mac ✓ Waiting ≤ 5m0s for control-plane = Ready ⏳Ĭreating a Kubernetes cluster is as simple as kind create cluster.įor more configuration of installation, please refer to KinD official documentation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
